From the intricate wiring of a skyscraper to the microscopic circuits governing a pacemaker, modern industry runs on electricity. But how do we design, build, and maintain these complex systems without getting tangled in a mess of wires and components? The answer lies in the elegant, universal language of electrical diagrams. These visual blueprints are indispensable, serving as the bedrock for understanding, troubleshooting, and innovating across countless sectors. Delving into the vast applications of electrical diagrams in various industries reveals their critical role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability everywhere electricity flows.
At a Glance: Why Electrical Diagrams Are Non-Negotiable
- Clarity & Understanding: They simplify complex electrical systems into an easy-to-read visual format.
- Rapid Troubleshooting: Pinpoint problems quickly, reducing downtime and costly repairs.
- Enhanced Safety: Guide safe installation, maintenance, and repair, preventing accidents.
- Standardized Communication: Ensure everyone—from designers to technicians—is on the same page globally.
- Efficient Design: Essential for planning new systems, upgrades, and modifications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Crucial for meeting industry standards and legal requirements.
The Unsung Hero: Why Electrical Diagrams Matter More Than You Think
Imagine trying to assemble a complex piece of furniture without instructions, or navigating an unknown city without a map. Now, amplify that complexity by a thousand, and you're close to the challenge of working with electrical systems sans diagrams. Electrical diagrams are the meticulously drawn maps, the precise instructions, and the universal language that makes the invisible flow of electricity tangible and manageable. They transform abstract concepts into actionable intelligence.
As TechBullion aptly puts it, these diagrams are "indispensable tools" that offer a clear "visual representation of electrical circuits, making it easier to understand and troubleshoot electrical systems." Without them, even the simplest electrical task becomes a guessing game, prone to errors, delays, and significant safety risks. They aren't just technical drawings; they're foundational to how we harness and control power.
Deciphering the Blueprint: Key Types of Electrical Diagrams
Before we dive into their industry-specific applications, let's quickly clarify the main types of electrical diagrams you'll encounter. Each serves a distinct purpose, offering different levels of detail and perspectives on an electrical system. Understanding these distinctions is key to knowing which diagram to reach for.
Schematic Diagrams: The "How It Works" View
Think of a schematic diagram as the theoretical heart of an electrical system. It shows you the components (resistors, capacitors, switches, power sources) and their functional connections, often using standardized symbols. What it doesn't show is their physical location or exact wiring path. It's about the logical flow of electricity and how the circuit is supposed to operate. Engineers use these extensively during the design phase to conceptualize and validate circuit behavior. They answer the question: "How does this circuit function?"
Wiring Diagrams: The "Where Everything Goes" Map
If a schematic tells you what components are connected, a wiring diagram shows you how they're physically connected. These diagrams provide a more realistic layout, illustrating the actual wires, terminals, and physical arrangement of components within a system or device. You'll see wire colors, connection points, and even cable routing. Technicians rely heavily on wiring diagrams for installation, maintenance, and especially for pinpointing physical breaks or misconnections. They answer: "Where does this wire go, and what does it connect to?"
Block Diagrams: The "Big Picture" Overview
Block diagrams zoom out, offering a high-level, simplified view of a system. They represent major functional parts of a system as blocks and show the relationships and signal flow between them, without delving into the intricate details of individual components or connections. These are excellent for understanding system architecture, identifying subsystems, and explaining overall operation to non-technical stakeholders. They answer: "What are the main parts of this system, and how do they interact?"
To truly master the language of these diagrams, you'll need to understand the symbols. Familiarizing yourself with the standardized diagram of electrical symbols is an essential first step, as they are the alphabet and vocabulary of electrical communication.
Industry by Industry: Where Electrical Diagrams Power Progress
Now, let's explore how these powerful visual tools are put to work across a diverse range of industries, shaping everything from our daily commutes to life-saving medical procedures.
Automotive Sector: Keeping Our Vehicles Running Smoothly
Modern vehicles are essentially computers on wheels, packed with complex electrical and electronic systems. From the engine control unit (ECU) managing fuel injection to the intricate wiring of infotainment systems, every function relies on precisely controlled electrical signals.
- Design & Manufacturing: Engineers use electrical diagrams to design every circuit, from power distribution to sensor networks and diagnostic ports. These diagrams ensure that components are correctly integrated and that the vehicle meets stringent safety and performance standards.
- Diagnostics & Repair: When your "check engine" light comes on, a technician's first step often involves consulting an electrical wiring diagram. These diagrams allow them to trace circuits, test components, and quickly isolate faults in everything from anti-lock braking systems (ABS) to power windows. Without them, troubleshooting an intermittent fault in a modern car's CAN bus system would be a nightmare, turning hours of skilled work into days of guesswork.
- Aftermarket Modifications: Adding a new sound system, tow hitch wiring, or auxiliary lighting? Electrical diagrams are crucial for safely integrating new components without damaging existing systems or creating electrical hazards.
Manufacturing & Industrial Automation: The Pulse of Production Lines
Automated factories are marvels of synchronized motion, powered by sophisticated control systems. Electrical diagrams are the backbone of this automation, orchestrating everything from robotic arms to conveyor belts.
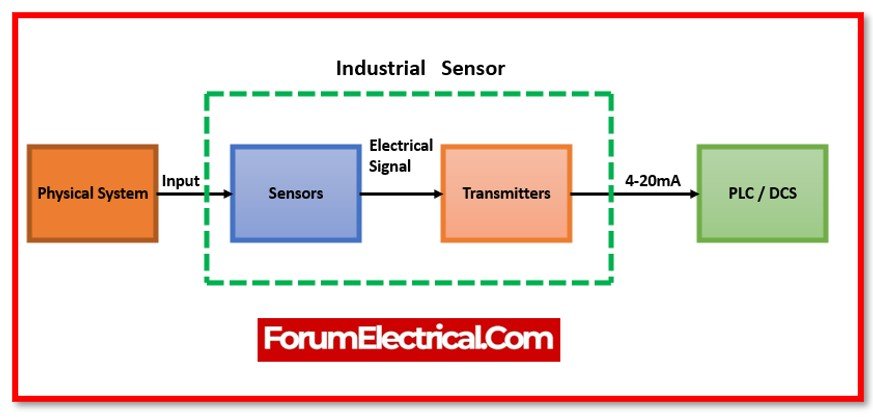
- Process Control: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) are at the heart of industrial automation. Their programming and wiring are entirely dependent on detailed electrical schematics and wiring diagrams. These diagrams illustrate the connections between sensors, actuators, motors, and control units, enabling engineers to design, implement, and monitor complex production processes.
- Maintenance & Downtime Reduction: When a production line grinds to a halt, every minute costs money. Maintenance technicians rely on electrical diagrams to rapidly diagnose motor control issues, sensor failures, or wiring shorts. A well-annotated diagram allows them to trace the fault, replace the defective component, and get the line running again, minimizing costly downtime.
- Safety Systems: Emergency stop circuits, interlocks, and safety light curtains are critical components of industrial safety. Electrical diagrams clearly depict these circuits, ensuring they are correctly installed, maintained, and function as intended to protect personnel and equipment.
Construction & Architecture: Bringing Buildings to Life
From residential homes to commercial skyscrapers, every building relies on a vast, interconnected electrical nervous system. Electrical diagrams are indispensable throughout the construction lifecycle.
- Electrical System Design: Architects and electrical engineers use diagrams to plan power distribution, lighting circuits, HVAC controls, security systems, and data networks. These plans ensure adequate power capacity, proper wiring routes, and compliance with building codes and safety regulations.
- Installation: Electricians on site follow detailed wiring diagrams to install conduits, pull wires, mount fixtures, and connect panels. These diagrams prevent costly mistakes, ensure correct component placement, and streamline the installation process.
- Maintenance & Upgrades: Over the lifespan of a building, electrical systems require maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Having accurate "as-built" electrical diagrams is vital for identifying circuits, safely troubleshooting issues, and planning renovations or additions without disrupting existing services. This includes everything from finding the right breaker for an outlet to integrating new smart home technologies.
Aerospace & Defense: Where Precision is Paramount
In industries where failure is not an option, electrical diagrams are elevated to an art form of precision and reliability. Avionics, spacecraft, and advanced defense systems demand meticulous electrical engineering.
- System Design & Integration: Aircraft and spacecraft are packed with redundant and highly complex electrical systems for navigation, communication, flight control, and power generation. Electrical diagrams are used to design every subsystem, ensuring interoperability, fault tolerance, and adherence to incredibly strict performance and safety standards.
- Manufacturing & Assembly: Technicians follow detailed wiring harnesses diagrams and schematics to assemble the millions of wires and components that make up an aircraft's electrical system. Any error can have catastrophic consequences, making the accuracy of these diagrams absolutely critical.
- Maintenance & Certification: Regular inspections and maintenance are vital for aerospace safety. Electrical diagrams are used for diagnostics, repairs, and even for simulating system behavior during certification processes. Tracing a fault in a fighter jet's radar system or a satellite's power supply would be impossible without these detailed maps.
Energy & Utilities: Powering Our World
The generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity across vast grids are monumental feats of engineering. Electrical diagrams are fundamental to the operation and stability of these vital infrastructures.
- Power Plant Operations: Within power plants (be it fossil fuel, nuclear, or renewable), complex electrical diagrams detail everything from generator connections to control systems for turbines, transformers, and switchgear. Operators use them for monitoring, control, and fault isolation.
- Grid Management: Electrical diagrams map the intricate network of transmission lines, substations, and distribution feeders. These are essential for grid operators to understand power flow, manage loads, isolate faults during outages, and plan maintenance without causing widespread blackouts. The rise of smart grids further increases the complexity, making dynamic, up-to-date diagrams even more crucial.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar farms and wind turbines connect to the grid through sophisticated inverter and control systems. Electrical diagrams are vital for designing these interconnections, ensuring stable power delivery and compliance with grid standards.
Telecommunications & IT: The Backbone of Connectivity
Our digitally connected world relies on a vast, intricate web of telecommunications and IT infrastructure. Data centers, network hardware, and communication systems are densely packed with electrical components.
- Data Center Design: Building a modern data center requires meticulous planning of power distribution units (PDUs), uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), cooling systems, and server rack wiring. Electrical diagrams ensure proper load balancing, redundancy, and cooling capacity, preventing costly downtime.
- Network Infrastructure: From fiber optic cables to wireless access points, the electrical power and signal routing for telecommunications equipment are detailed in diagrams. These are crucial for installation, upgrades, and troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
- System Integration: Integrating various communication protocols and hardware components requires clear electrical schematics to ensure compatibility and correct signal transmission, from cellular base stations to satellite communication arrays.
Marine & Shipbuilding: Navigating the Seas
Ships, from small recreational boats to massive cargo vessels, operate in challenging environments where reliability is paramount. Their electrical systems power everything from navigation and propulsion to communication and creature comforts.
- Vessel Design & Construction: Shipbuilders use electrical diagrams to design and install complex electrical systems, including main power distribution, engine controls, navigation equipment, safety systems, and specialized onboard machinery. Diagrams must account for harsh marine conditions, vibration, and potential exposure to saltwater.
- Maintenance at Sea: Far from land, maritime engineers must be able to diagnose and repair electrical faults. Comprehensive diagrams are their lifelines, enabling them to troubleshoot power outages, equipment malfunctions, or instrument failures efficiently, ensuring the vessel's safe operation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Marine vessels are subject to strict international regulations for safety and environmental protection. Electrical diagrams are critical for demonstrating compliance with standards set by organizations like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and classification societies.
Medical Devices: Precision for Life
In the realm of healthcare, electrical diagrams take on an even more profound importance, directly impacting patient safety and the accuracy of diagnoses and treatments.
- Device Design & Manufacturing: From MRI machines and X-ray systems to pacemakers and defibrillators, medical devices are engineered with extreme precision. Electrical diagrams detail the intricate circuitry, sensor connections, power management, and user interfaces. This meticulous design ensures the devices operate reliably and safely, meeting rigorous regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, CE).
- Installation & Calibration: Hospitals and clinics rely on highly accurate installation and calibration of medical equipment. Electrical diagrams guide technicians through these processes, ensuring that life-support systems, diagnostic tools, and monitoring equipment function perfectly.
- Troubleshooting & Repair: When a critical piece of medical equipment malfunctions, quick and accurate troubleshooting is essential. Electrical diagrams allow biomedical engineers to identify faulty components, understand signal pathways, and perform repairs that maintain the device's integrity and patient safety. A single misplaced wire could lead to a misdiagnosis or a critical failure.
Consumer Electronics: The Gadgets We Love
Finally, electrical diagrams play a crucial role in the devices we use every day, from smartphones and laptops to home appliances.
- Product Development: Engineers use schematics to design new electronic gadgets, laying out the integrated circuits, power management systems, and user interface components. These diagrams are iterated upon to optimize performance, size, and power consumption.
- Repair & Reverse Engineering: When your old gaming console or favorite speaker breaks, repair technicians often consult service manuals that include electrical diagrams. These diagrams are invaluable for diagnosing component failures or identifying short circuits, helping to extend the life of consumer products. For hobbyists and developers, diagrams can also aid in understanding how existing devices work, inspiring new innovations.
Mastering the Language: Best Practices for Using Electrical Diagrams
Merely possessing an electrical diagram isn't enough; you need to know how to effectively use it. This skill separates the competent professional from someone simply looking at lines on a page.
Familiarize Yourself with Symbols
As mentioned by TechBullion, this is foundational. Every component—from a resistor to a relay—has a standardized symbol. Learning these symbols is like learning the alphabet of a new language. Before you even try to "read" a diagram, spend time understanding its legend and common industry symbols. There are international standards (like IEC and ANSI) that govern these symbols, ensuring global consistency.
Follow the Flow
Electricity has a starting point (the power source) and a path it takes. When analyzing a diagram, always trace the current's flow from the power source, through switches, protective devices (fuses/breakers), loads (motors, lights), and back to the source or ground. This systematic approach helps you understand the circuit's intended operation and identify where the flow might be interrupted or diverted.
Look for Anomalies
When troubleshooting, a diagram becomes your comparison tool. You compare the physical reality of the system to what the diagram depicts. Are all wires connected as shown? Are component values correct? Are there any unexpected connections or disconnections? TechBullion rightly points out that diagrams help you "identify any irregularities or deviations from the expected connections." This contrast between the "as-designed" and "as-is" is often where problems are revealed.
Cross-Referencing and Version Control
Complex systems often have multiple diagrams (schematics, wiring, block diagrams, component layouts). Learn to cross-reference information between them. For instance, a schematic might tell you what a component does, while a wiring diagram tells you where it's physically located. Always ensure you're using the most current version of a diagram. Outdated diagrams are a common source of confusion and errors, especially in systems that undergo frequent modifications.
Leverage Digital Tools
While paper diagrams have their place, modern software tools for CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and ECAD (Electronic Design Automation) offer immense advantages. They allow for easy modification, version tracking, simulation, and integration with other design tools. Learning to navigate these digital environments can significantly boost efficiency and accuracy.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Despite their undeniable value, working with electrical diagrams isn't without its hurdles. Recognizing these challenges and knowing how to tackle them makes you a more effective professional.
Outdated or Inaccurate Diagrams
The Problem: Systems evolve. Components are replaced, wires rerouted, and modifications made. Often, the documentation isn't updated, leading to a discrepancy between the diagram and the actual system. This is incredibly dangerous and time-consuming.
The Fix: Implement strict version control protocols. Whenever a modification is made, however small, ensure the "as-built" documentation is updated immediately. Regular audits comparing physical installations to diagrams can also catch discrepancies early. Encourage technicians to report any inconsistencies they find.
Lack of Standardization
The Problem: Different manufacturers, designers, or even countries might use slightly different symbols or conventions, leading to confusion.
The Fix: Prioritize using diagrams that adhere to recognized international standards (e.g., IEC, ANSI). If working with older or non-standardized diagrams, create a comprehensive legend for symbols and abbreviations unique to that documentation. Provide training on these specific conventions to ensure clarity.
Complexity Overload
The Problem: A single diagram for a highly complex system can be overwhelming, packed with so much information it's hard to follow.
The Fix: Good design practices dictate breaking down complex systems into smaller, manageable sub-circuits or modules. Utilize block diagrams for overall understanding, then drill down into detailed schematics for specific sections. Color-coding and clear annotation can also significantly improve readability.
Training Gaps
The Problem: Even with perfect diagrams, if personnel don't know how to read them, their value is lost.
The Fix: Invest in continuous training. Regularly refresh skills on symbol recognition, tracing circuits, and troubleshooting methodologies using diagrams. Practical exercises and hands-on scenarios are invaluable for building confidence and competence.
The Future of Electrical Diagrams: Smart, Dynamic, & Integrated
The world of electrical diagrams isn't static. As technology advances, so too do the tools and methods for creating and interacting with these essential blueprints. We're on the cusp of a new era where diagrams are more intelligent, dynamic, and seamlessly integrated into our physical and digital workspaces.
- AI-Assisted Design: Artificial intelligence is beginning to aid in the automated generation and optimization of electrical diagrams, identifying potential errors or inefficiencies in the design phase. This can accelerate development cycles and improve design quality.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for Troubleshooting: Imagine pointing your tablet or AR glasses at a complex control panel, and the electrical diagram overlays directly onto the physical components. This "x-ray vision" can highlight specific wires, show real-time sensor data, or guide repair steps, revolutionizing field diagnostics and maintenance.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) Integration: In construction, electrical diagrams are becoming increasingly integrated into comprehensive BIM models. This allows for a holistic view of a building's entire infrastructure, enabling better coordination between electrical, mechanical, and structural disciplines, and improving lifecycle management.
- Digital Twins: Creating digital replicas (digital twins) of physical systems, complete with their electrical diagrams, allows for virtual testing, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring, reducing the need for physical prototypes and costly downtime.
Your Essential Toolkit for Navigating Electrical Systems
Electrical diagrams are far more than just lines and symbols on a page; they are the intellectual scaffolding upon which all modern electrical infrastructure is built. From the smallest circuit board in your smartphone to the colossal power grids that span continents, these diagrams provide the clarity, safety, and standardization essential for progress.
Whether you're an engineer designing the next generation of electric vehicles, a technician troubleshooting a factory automation line, or an electrician wiring a new building, your ability to read, interpret, and apply these diagrams is a direct measure of your effectiveness and your contribution to a safer, more efficient world. The journey into the applications of electrical diagrams in various industries reveals a fundamental truth: to master electricity, you must first master its language. So, invest in learning those symbols, practice tracing those circuits, and always demand the most accurate blueprint. Your success—and the safety of those around you—depends on it.